Introduction
Kaizen is an approach to creating continuous improvement based on the idea that small, ongoing positive changes can reap significant improvements. Typically, it is based on cooperation and commitment and stands in contrast to approaches that use radical or top-down changes to achieve transformation.
Script
The little things add up. The word Kaizen is derived from two Japanese words that loosely translate to “good change” or “improvement.” And in the context of lean management, continuous improvement. While lean management seeks to eliminate wasteful processes, Kaizen is the concept of creating small positive changes to eventually reap major improvements.
Kaizen is not one specific methodology, but rather an attitude based on cooperation and commitment instead of radical top-down transformations.
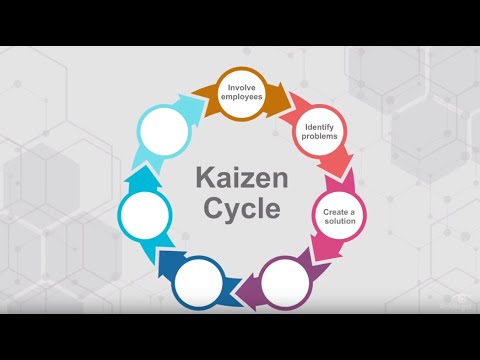
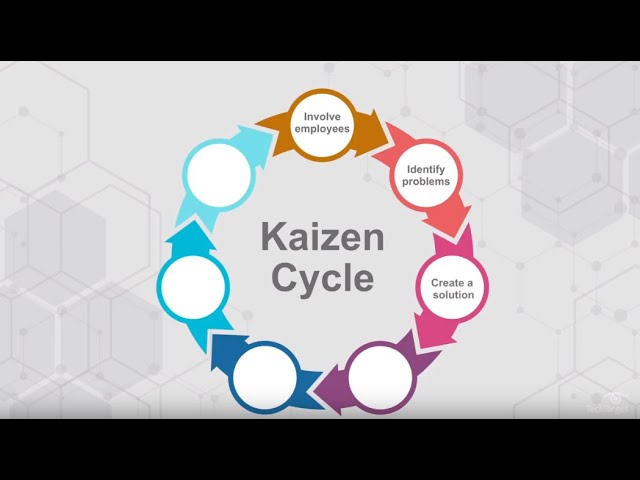
Kaizen is rooted in the belief that everything can always be improved, nothing is status quo, and adaptation trumps perfectionism. Specifically, the Kaizen Cycle has seven steps:
- Involve employees to crowdsource issues and problems
- Identify problems and potential opportunities
- Create a solution encouraging ideas from all employees
- Test the solution with the help of all employees
- Analyze the results at various intervals and determine the success level
- Standardize and adopt the solution if results are positive
- And repeat the cycle for all future problems
The main advantages of Kaizen including gentle approach to change that avoids resistance and abandonment, waste reduction, improved morale and teamwork, and an increase in customer requirement awareness, resulting in a shift in client focus.
However, it’s not a perfect fit for every organization, especially those with territorial culture and closed communications. And short-term Kaizen methods might create a shallow fleeting burst of excitement before it gets abandoned.
Does your organization practice Kaizen? Tell us all about it in the comments below and remember to hit that like button.
Quiz
Resources
Discussion
Which of the below points do you feel are the most difficult to implement? Give your reasons.
10 principles of Kaizen
Because executing Kaizen requires enabling the right mindset throughout a company, 10 principles that address the Kaizen mindset are commonly referenced as core to the philosophy. They are:
- Let go of assumptions.
- Be proactive about solving problems.
- Don’t accept the status quo.
- Let go of perfectionism and take an attitude of iterative, adaptive change.
- Look for solutions as you find mistakes.
- Create an environment in which everyone feels empowered to contribute.
- Don’t accept the obvious issue; instead, ask “why” five times to get to the root cause.
- Cull information and opinions from multiple people.
- Use creativity to find low-cost, small improvements.
- Never stop improving.
Ask Al-i
- Who invented the Kaizen method?
- How can employees be included in the Kaizen process to identify problems?
- How can companies measure the success of Kaizen initiatives?
- How can organizations overcome resistance to implement Kaizen principles?